Issues of safety and cybersecurity have become major concerns of today’s technology-based economies. Cyber safety and security have become a core need to provide a sustainable and safe society for online users in cyberspace.
Considering the rapid increase in technology deployment, cybersecurity has become a global necessity in the effort to regulate protective measures, whether direct or indirect, to Prevent systems from cyber attacks.
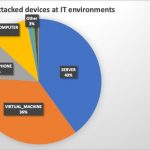
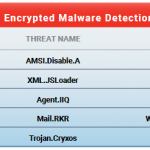
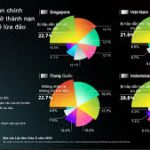
Cyber security threats are increasing
Cybersecurity includes adopting and maintaining processes related to early detection of cyber threats and mitigation of risks, which is a prerequisite for adopting a computing ecosystem. Responsible sustainability protects the functioning of modern technology-based societies. According to the World Economic Forum’s 2019 Global Risk Report, cyber security attacks are now among the top risks globally.
Cyber attacks can lead to billions of dollars in losses in the business sector, especially when servers of banks, hospitals, power plants and smart devices are compromised. This could lead to serious damage to the digital society instead of supporting development. The lack of or inadequate security measures may not cause serious incidents initially, but digital society will gradually lose trust, leading to a serious decline in development. According to the World Economic Forum, the estimated market value of cybersecurity is expected to increase from 120 to 300 billion by 2024.

Network safety and security aim to protect data from attackers, which is very important for all individuals and organizations. This is an integral part of cyber threat mitigation strategies. The most important thing is to achieve sustainability in cyberspace, thereby securing data and protecting information. All countries around the world are concerned about protecting their data environments from hackers and malware – which can be linked to the impact of the massive ransomware wave in recent years.
Cyber threats are increasing rapidly with sophisticated and sinister plots and are the motivation to infiltrate information systems. Understanding and identifying security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cyber espionage has become a common requirement for security professionals. The impact of intrusions can bring organizations to a halt and be devastating. The mindset of the cybersecurity community has shifted from “if we get attacked” to “when we get attacked”: be prepared instead of expecting that cyberattacks are completely avoidable. Achieve and maintain effective network information security despite attacks.
Measures to ensure network security and safety
Techniques such as phishing, spamming and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks are frequently used by cybercriminals to harm data environments and monitor systems, so it is necessary to plan strategies continuous monitoring strategy. Understanding cybercrime and cyber safety and security is imperative to developing effective offensive and defensive security countermeasures. According to McAfee, the introduction of law enforcement and regulatory frameworks, education and awareness programs, as well as well-developed technological innovations can be the best option to fight cybercrime.
With the nature of Internet usage today, whether for social media or e-commerce applications, cybercriminals can find weak points to commit crimes, from stealing data personal data to community data breaches. Especially hacking tools are freely available and software vulnerabilities are publicly disclosed without comprehensive preventative measures. This is the reason for the development of the Comprehensive Community Cyber Security Model (CCSMM), which helps bridge the gap by guiding users to recognize cyber safety and security requirements. community, and ultimately create a viable and sustainable cybersecurity program.
The ability to identify and manage cybersecurity risks in a timely manner is critical to the success and survival of any organization. All individuals in the organization need to participate in network security and safety risk management to be able to properly identify and assess risks (must be classified and prioritized). Cyber risk assessment is critical to providing organizations with a clear and accurate picture of all relevant security risks, which is the basis for cyber situational awareness.
A safe, sustainable cybersecurity posture relies on continuous risk management, including continuous monitoring and data collection. By using governance, risk and compliance (GRC) monitoring tools, cyber security risk levels can be monitored and assessed. When described in the context of assets, threats, and vulnerabilities, risks can be detailed by the most widely deployed, purpose-built knowledge organization systems where is Structured Threat Information Expression (STIX). STIX identifies objects such as attack types, indicators and malware, intrusion collections, risk factors, security vulnerabilities, etc. and can also capture the relationships between these objects.
Data classification also helps organizations determine the cost and effort involved in ensuring critical information assets are used by management for decision making. This involves identifying and cataloging critical data and establishing user access with the principle of least privilege.
It is important to regularly evaluate security controls in place through mock attack techniques, such as penetration tests, thus strengthening the overall security infrastructure . Planning for data breaches is also important, requiring the establishment of an incident response team. Security mechanisms that prevent data intrusion are also needed. If a data breach occurs, it is important to identify the source of the attack and the company’s data security levels. The proposed comprehensive approach includes six steps: simulation, analysis, planning, development, construction, and operations. The first two phases, simulation and analysis, contribute to the development of a sustainable protection plan; The third stage is planning; The final phase is implementation, addressing the provision and building of the necessary resources to protect the system against cyber attacks.
Government agencies need to get involved in the event of a cyber incident that affects computer users on a large scale, such as cyber attacks that cause complete paralysis in some sectors. Besides, being ready to limit attacks, detect, respond and recover from cyber attacks is essential. By implementing an effective and stable security management system, cyber risks can be minimized; However, regardless of the type of security system implemented, there is always a probability of a data breach. It is important to emphasize that IT security is not the sole responsibility of the IT department but is a shared responsibility of the entire organization.
Some outstanding trends in network safety and security
Industrial control systems (ICS)
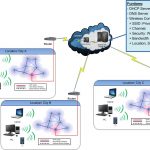
Ensuring safety and network security in industrial control systems (ICSes) is developed more slowly than IT systems. ICS is already used in some control systems as a basic component. However, various ICS security issues remain unresolved due to the reliance on control network-based platforms. ICSes brought a change in software design by merging commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) operating systems (OSes) and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). They are intended to replace proprietary network components.
Some ICS have applied wireless network technology to enable remote device access, support and maintenance. Although this is a technological advancement, it also makes it difficult to maintain confidentiality and protect the integrity of data transmitted across network nodes. This introduces vulnerabilities and increases the risk of potential security incidents. Factory control systems must be directly connected to the enterprise IT system so that information can be shared via Ethernet and TCP/IP. This allows operators to remotely monitor production facilities via secure wireless devices to perform operational management activities. There are several ways to implement cybersecurity measures both in ICS and in IT systems.
However, ICS implementations are more challenging due to their need for continuous operation, proprietary system architecture, vendor-specific software, limited resources, processing capabilities, and physical network nature of the control system.
These are the main reasons industrial control systems are designed to prioritize availability, security implementation needs to consider the potential impact on system performance and productivity. To secure ICS, security mechanisms, often called defense-in-depth, must be built multi-layered around the controller. The fewer the number of integrated services and the number of connections to the central controller (restricting network services, closing connection ports), the lower the likelihood of security breaches in defense layers. Only when TCP ports are secured is TCP port communication allowed in the application layer.
This strategy can successfully protect systems even against zero-day attacks, which are notoriously difficult to analyze. The intensity of cyber attacks is increasing at a rapid pace, and many target military, financial, and energy infrastructure. Therefore, ensuring the safety of these control systems is a challenging issue and a trend that is receiving attention in the current period.
Smart grid is an electrical system designed to achieve reliability, flexibility, efficiency and provide high-performance and stable power supply. The use of renewable energy sources has been increasing exponentially to generate more energy globally. The most important component that needs to be protected from cybercriminals in a smart grid is the signal transmission network, as it is based on a real-time information sharing system.
The maintenance and control functions of the power grid also depend on this particular component. As defined by the European Technology Platform, a smart grid is a type of electricity network that takes into account user actions to efficiently provide and share safe, sustainable and affordable electricity supplies. Economic benefits for all connected entities. The International Council on Large Power Systems and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have worked for a decade on issues related to safety and cybersecurity in power systems. IEC Technical Committee 57 (IEC TC57) has developed a security standard to identify security issues for individual operations of power systems and transmission channels. The development of smart grid technology involves traditional power generation, transmission networks, along with distribution networks. It is important to have current parallel to the signal flow in the transmission network, allowing for optimized operation. Substations are nodes that link all the cables and lines to distribute electricity in the electrical network. Typically, these stations receive data and transfer information between sensors or transmission devices present in the power grid.
During the 1980s, power grid architecture gradually evolved from the use of copper wires to the direct use of support solutions established by modem technology. Conventional supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems have a series of alarming problems related to interoperability between devices, necessitating the need to refactor their protocols. In 1994, IEC and IEEE introduced a common standard for transmission systems. IEEE has also established the Utility Transmission Architecture (UCA) Framework and the IEC 61850 standard that defines communication protocols for transmission networks and systems. Updated versions of this standard were subsequently issued from 2002 to 2005.
Analysis of attack scenarios in recent years shows that the Stuxnet malware disrupted several industrial sites and a nuclear plant in Iran and is a known targeted cyber attack (APT). first into a SCADA system, not only performing cyber espionage but also taking partial control of the system’s operations. Notable variants of Stuxnet include Duqu, Flame, and Gauss.
Such computer viruses can even start a cyber war. There is a saying that “when the power stops, everything stops”, this is something that needs special attention as power grid systems are developing thanks to IT applications, including solutions for control devices. . These technology solutions reduce the cost of deploying power grid systems, but increase security vulnerabilities. Currently, there are many security measures and tools to prevent unauthorized access to substation control systems. The measures mainly focus on firewalls and one-way security gateways (which have very unique physical layer security with transmitters and receivers).
These devices can be installed in both control networks and networks of agencies and organizations. The application of laser and photocell technology in both devices can limit communication from receiver to transmitter, but allows two-way communication and prevents exploitation of vulnerabilities over the network. However, constant changes in the transmission network make it difficult to maintain adequate firewalls and security gateways at all points.
The IEC 62351 security standard has outlined the security mechanism for maintaining communications established in the above mentioned IEC 61850. However, this network security and safety mechanism clearly affects the performance of real-time communication in the substation. The growing needs of the power industry require a basic security framework and further optimized security solutions to protect data, as well as maintain all information transmission taking place within the power industry. smart power grid.
Emerging trends: Blockchain and IoT
Blockchain is a distributed ledger based on cryptography, which is considered to have a permanent impact, as it allows trusted transactions between participants in the network. The unique features of this technology have attracted the attention of various fields and its application is considered one of the best options for a wide range of contexts. Presents a systematic literature review and description of how and where Blockchain can contribute to sustainable and secure cybersecurity measures. Three research questions need to be clarified to deploy blockchain in network safety and security:
What are the recent and latest applications of Blockchain in the field of security? How is this technology used to improve network safety and security? What are the methods available for blockchain-related solutions in managing security without the need for cryptocurrency tokens?
Some key safety and cybersecurity applications of blockchain include:
IoT: deployments can be secured through peer-to-peer (P2P) authentication of the network and connected devices, including risk detection and malware prevention. Data sharing and storage: ensure that cloud data remains intact and no unauthorized access can occur; list of hash functions that enable secure search and exchange of secured and verified data from sender to receiver. Cyber security: Blockchain data authentication is central because data is stored in a decentralized manner. Navigating access and extension of the World Wide Web: ensuring the validity, use and navigation of interconnected wireless Internet access points by forwarding to appropriate websites and applications web applications through encrypted, secure techniques.
Blockchain, with its ability to store immutable transaction records and unique decentralized nature can be effectively used to ensure safety and cybersecurity measures in a system. Each member of a blockchain has an absolute copy of the entire chain of transactions. Any changes to the chain can only be made when the members of the chain agree to the correction in the previously arranged chain. Implementing security through P2P during data exchange through authentication and identification is accepted. Blockchain can act as an intermediary between two network layers: application layer and transport layer, the owner has full control over the data.
Blockchain is increasingly being used to ensure a sustainable network by handling software-defined networks (SDN). Storage pools are also used to authenticate important data for secure storage in a decentralized manner. However, the immutable nature of blockchain makes the technology difficult to apply in systems with data privacy risks.
With the aim of applying Blockchain in safety and network security applications, researchers found that using multiple layers of blockchain can ensure the reliability of authenticated transactions. Systems based on synchronization mechanisms are those that can allow the application of security measures to be extended to all levels of the network.
The above benefits also come with some major challenges related to implementing blockchain applications such as: costs, blockchain governance and other factors (including scalability, bandwidth limitations). ). Only by addressing the above challenges can blockchain bring about significant change to future systems.
Smart cities include bringing together all the administrative, civic, social, health and educational systems and every other important element of the city’s surroundings, under technological control. information and communication (ICT). This is done by combining advanced integration technologies and IoT devices with networking, monitoring, control and various selection algorithms.
The basic challenges of smart cities related to safety and cybersecurity include:
IoT tools: radio frequency identification, wireless sensor networks, smart mobile phones, and smart grids. Reasons from management activities: secure infrastructure, flexibility and ability to manage smart devices. Economic and social aspects: intelligent communication; services, privacy and e-commerce.
A number of international research projects have mentioned the concept and concerns about safety and cybersecurity for smart cities on a large scale. A Cybersecurity Architecture for Hybrid Smart Cities (HSCCA) has been proposed to ensure risk management at the regional level by improving efficiency, ease of access and detection and handling. In general, this architecture only refers to an optimally designed smart city model that takes into account all plans related to safety and cybersecurity and assumes the elimination of all security vulnerabilities. information security, availability and flexibility.
The role of artificial intelligence in sustainable network safety and security
Artificial intelligence, and especially machine learning, offers advances in cybersecurity, but is difficult for the broader community to adopt and understand. The application of artificial intelligence in network safety and security includes both opportunities and challenges. A cybersecure, autonomous machine learning platform for anomaly detection (CAMLPAD) has been proposed to detect risks and attacks in real time. CAMLPAD is a model that combines diverse network data used for model development, including YAF, BRO, SNORT, PCAP, and Cisco Meraki. This model can not only detect anomalies but also determine the threat level of potential security breaches.
Currently, the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in safety and cyber security products and services has been widely applied around the world. Many businesses have provided products and services to the market with remarkable results. Artificial intelligence application in the future will soon become a core factor to ensure safety and network security of international products and services.

Vina Aspire is a consulting company, providing IT solutions and services, network security, information security & safety in Vietnam. Vina Aspire’s team includes skilled, qualified, experienced and reputable experts and collaborators, along with major domestic and foreign investors and partners to join hands in building.
Businesses and organizations wishing to contact Vina Aspire Company with the following information:
Email: info@vina-aspire.com | Website: www.vina-aspire.com
Tel: +84 944 004 666 | Fax: +84 28 3535 0668
![]()
Vina Aspire – Vững bảo mật, trọn niềm tin














 …
…